코드:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
x_raw = [[1, 2, 1, 1],
[2, 1, 3, 2],
[3, 1, 3, 4],
[4, 1, 5, 5],
[1, 7, 5, 5],
[1, 2, 5, 6],
[1, 6, 6, 6],
[1, 7, 7, 7]]
y_raw = [[0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0]]
x_data = np.array(x_raw, dtype=np.float32)
y_data = np.array(y_raw, dtype=np.float32)
nb_classes = 3
tf.model = tf.keras.Sequential()
tf.model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(input_dim=4, units=nb_classes, use_bias=True)) # use_bias is True, by default
# use softmax activations: softmax = exp(logits) / reduce_sum(exp(logits), dim)
tf.model.add(tf.keras.layers.Activation('softmax'))
# use loss == categorical_crossentropy
# SGD == standard gradient descendent, lr == learning rate
tf.model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=0.1), metrics=['accuracy'])
tf.model.summary()
history = tf.model.fit(x_data, y_data, epochs=2000)
print('--------------')
# Testing & One-hot encoding with argmax(return hot index)
a = tf.model.predict(np.array([[1, 11, 7, 9]]))
print(a, tf.keras.backend.eval(tf.argmax(a, axis=1)))
print('--------------')
b = tf.model.predict(np.array([[1, 3, 4, 3]]))
print(b, tf.keras.backend.eval(tf.argmax(b, axis=1)))
print('--------------')
c = tf.model.predict(np.array([[1, 1, 0, 1]]))
c_onehot = np.argmax(c, axis=-1)
print(c, c_onehot)
print('--------------')
all = tf.model.predict(np.array([[1, 11, 7, 9], [1, 3, 4, 3], [1, 1, 0, 1]]))
all_onehot = np.argmax(all, axis=-1)
print(all, all_onehot)
이전 sigmoid에서는 keras model을 사용하지 않았기 때문에 이번 softmax에서는 keras를 사용
결과:
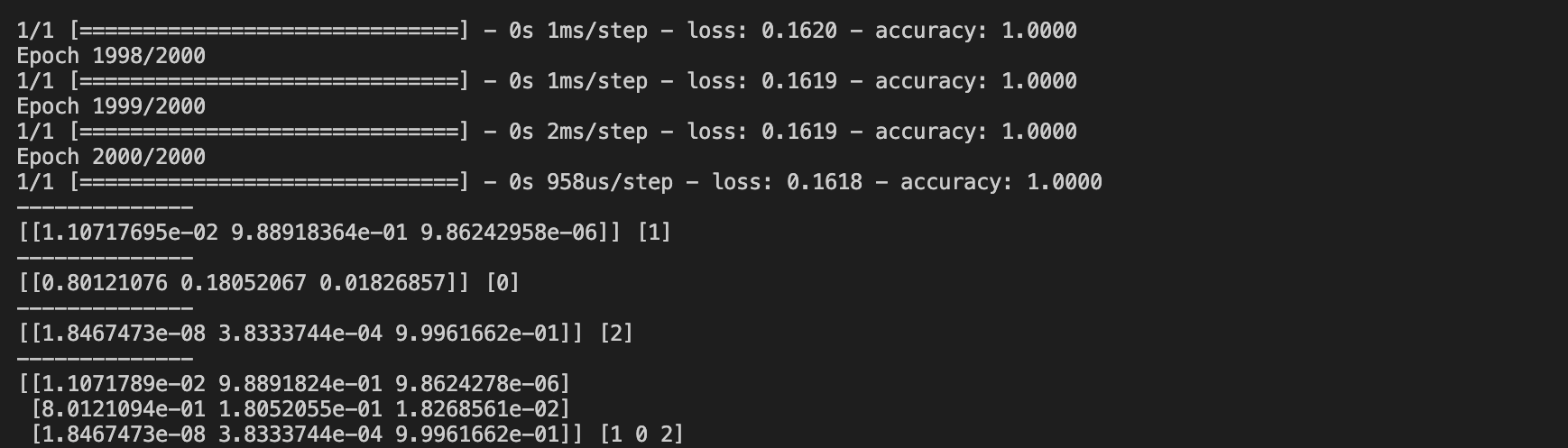
2000번 fitting을 완료한 후, multinominal classification의 prediction 결과를 출력했다. 첫 번째 input에 대한 prediction에서 array의 두 번째 값이 가장 크다. 따라서 결과는 [0, 1, 0]이 되고 one-hot encoding 결과는 1이다. 마찬가지로 두 번째 prediction은 [1, 0, 0]이고 마지막은 [0, 0, 1]이므로 3개의 input의 prediction에 대한 one-hot encoding 결과는 [1, 0, 2]가 된다.
# 참고 링크의 코드에서 one-hot encoding을 할 때, predict_classes를 사용하면 경고가 뜬다. 이때 numpy의 agrmax를 사용하면 된다. 사용법은 np.argmax(x, axis=-1)이다. 이 코드에서 x에는 prediction 객체가 들어간다. axis 인자는 행과 열의 계산 기준에 대한 옵션이다. 2차원에서 0은 열 방향, 1은 행 방향, -1은 마지막 axis인 1이므로 행 방향이 된다.

참고:
https://github.com/hunkim/DeepLearningZeroToAll/blob/master/tf2/tf2-06-1-softmax_classifier.py
'데이터 사이언스 공부 > 딥러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| CNN, RNN (0) | 2020.07.03 |
|---|---|
| ML Tip - Learning Rate, Overfitting, Regularization, Normalization, Standardization, Drop Out, Tensor Board (0) | 2020.06.26 |
| Logistic Regression, Binary Classification, Sigmoid (0) | 2020.06.16 |
| TensorFlow 2.0 basic practice 2 (0) | 2020.06.08 |
| TensorFlow 2.0 basic practice 1 (0) | 2020.06.04 |